Data Analysis
Data Fundamentals
In today’s rapidly developing digital era, data has become one of the most valuable assets of businesses and organizations. Data is the essential source of information that allows us to gain deeper insights into the nature of phenomena and social laws. From sciences, healthcare to business, education, transportation and many other fields, data plays a pivotal role in supporting decision-making and problem-solving. To be able to effectively harness the value of data, we need to firmly grasp the fundamental knowledge, known as “data fundamentals”.
Data is a collection of information, events, facts, or figures about an object, phenomenon, or system.
Data can exist in various forms, including text, images, sound, video, and numerical values.
Data is typically used to represent information, knowledge, or insights about a specific issue or to support the decision-making process. Data can be collected, stored, processed, and presented using various means, and it plays a crucial role in many fields, including science, engineering, business, healthcare, education, and many others. To analyze and utilize data effectively, appropriate tools and techniques are often required, such as data analysis, artificial intelligence, and machine learning.
“Data fundamentals” is a fundamental concept in the world of data science and information technology. It serves as the cornerstone of data analysis, interpretation, and decision-making processes. Understanding data fundamentals is crucial for anyone working with data, whether you’re a data scientist, analyst, or simply someone looking to make informed choices based on data-driven insights.
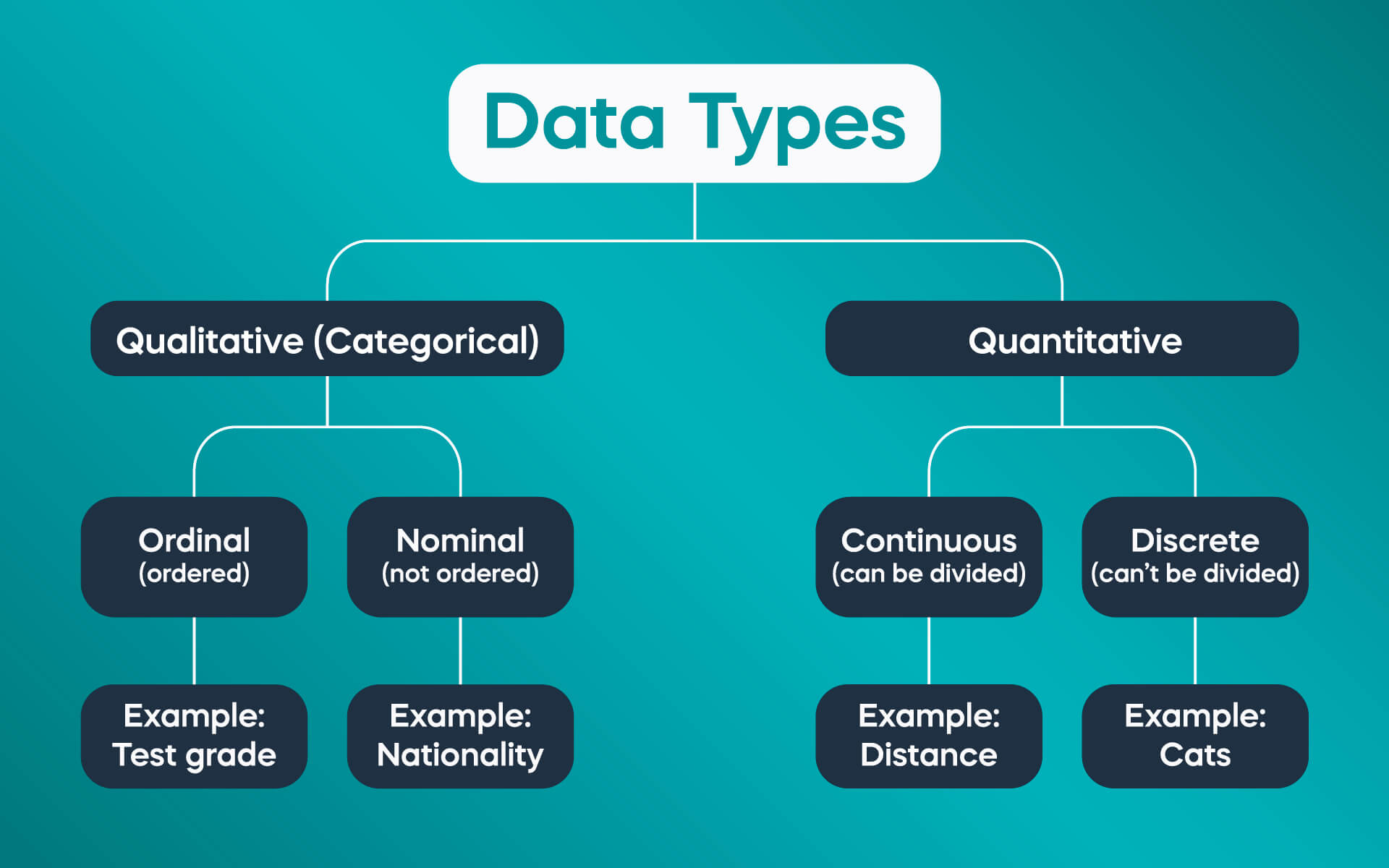
In essence, data fundamentals encompass two core concepts: qualitative data and quantitative data.
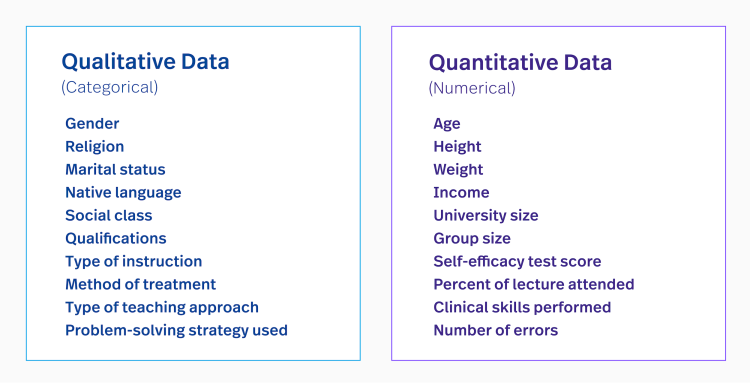
Qualitative data refers to the quality characteristics of objects and phenomena, which cannot be measured numerically. Typical examples are gender, nationality, ethnicity, religion, opinion evaluation, etc. Qualitative data is often collected in the form of text, images, audio, video.
In contrast, Quantitative data represents quantities and measurements in numbers. Examples are height, weight, age, revenue, profit, etc. Quantitative data allows computations, statistical analysis and comparison of figures.
Moreover, data fundamentals delve into data collection, storage, processing, and visualization techniques, as well as data quality and integrity. It’s the foundation upon which data professionals build their expertise, enabling them to extract meaningful insights, solve complex problems, and drive innovation in various industries.
Fundamental knowledge about data is the foundation for data experts and scientists to develop their expertise. Understanding data types thoroughly, knowing how to properly collect and process data will help them extract useful information, gain deeper insights into problems, thereby proposing effective solutions for complex challenges.
In today’s era when data has become an invaluable asset, a profound understanding of data’s basic principles is the key for individuals and organizations to unlock the value of data. Data only becomes meaningful when we know how to collect, select, analyze and apply it properly. Even for those who do not directly work in the data field, basic data literacy also helps them make wiser decisions at work and in life.
In conclusion, it can be asserted that mastering fundamental knowledge about data is extremely important for everyone in this modern age. It is the basis for all activities of collecting, analyzing, applying and developing data-driven solutions. Therefore, we need to spend time studying and grasping concepts, tools and techniques related to data. Having sufficient knowledge about data will enable us to work more easily and effectively in today’s big data era.


